soil moisture deficit|how is soil moisture measured : wholesaler Available Water Capacity (AWC) is the portion of water in a soil that can be readily absorbed by plant roots of most crops. Soil Moisture Deficit (SMD) or Depletion is the amount of water .
webLog on to VCC Continuing Studies portal to access your courses, programs, and student services. Whether you are looking for full-time, part-time, or online learning options, VCC .
{plog:ftitle_list}
There are no messages on IC_admin's profile yet. Loading.
The Soil Moisture Anomaly map shows the difference between the current and historical soil moisture deficits. SMD is calculated based on incoming daily rainfall (mm), outgoing daily .
Limited evapotranspiration due to soil drying further increases atmospheric aridity (vapor pressure deficit, VPD), which reduces the probability of precipitation.
Soil moisture is shown as a deviation from average soil moisture conditions from 2015–present. This map relies on remotely sensed soil moisture data derived from NASA missions ( SMAP ) to assess soil moisture conditions .
We focus on soil moisture deficits, which are indicative of associated impacts on ecosystems. Soil moisture is a key state variable of the land surface, reflecting complex . Accurate drought assessments are critical for mitigating the detrimental impacts of water scarcity on communities across the world. In many regions, deficits in soil moisture represent a key driver of drought conditions.Available Water Capacity (AWC) is the portion of water in a soil that can be readily absorbed by plant roots of most crops. Soil Moisture Deficit (SMD) or Depletion is the amount of water . In order to optimize the agricultural water use, we propose to develop indices (aridity index, soil moisture deficit index, crop water stress index) that are crucial for a farmer .
Both low soil water content (SWC) and high atmospheric dryness (vapor pressure deficit, VPD) can negatively affect terrestrial gross primary production (GPP). Yao et al. (2023) add the soil moisture to a similar analysis, and their results indicate that soil moisture was the factor most strongly associated with recovery duration, followed by temperature and vapor pressure deficit (VPD).
While drought is understood to be dry conditions persistent enough to cause crop damage or deficits in water resources, the severity or classification of deficit depends on the degree of moisture .A soil water deficit results from an imbalance between the supply and demand of soil moisture (Wang et al., 2011). Field sampling and simulation results showed a marked decrease in soil moisture after the conversion of farmlands to apple orchards ( Figs. 3 and 9 ), with previous studies reporting similar results ( Huang et al., 2018; Ouyang et . Various formulations are available in the literature to obtain water availability/deficit from soil moisture data (Seneviratne et al., 2010); a common feature of these formulations is to use a transformation of θ able to account for the fact that there is a soil moisture regime under which soil moisture is not a limiting factor (wet regime, θ .
Soil Moisture Deficit (SMD) is the amount of rain needed to bring the soil moisture content back to field capacity. Field capacity (SMD=0) is the amount of water the soil can hold against gravity i.e. the maximum water a pot plant can be watered and not leak water. Negative SMD indicates a water surplus, which will be drained over time through . They stated that severe soil water deficit significantly reduced the economical yield of wheat crop as compared to slight soil water deficit. They also stated that evapotranspiration of crop also depended on irrigation amount. Qiu et al. also observed WUE on the basis of photosynthesis and biomass production and found a positive correlation . The terrestrial carbon and water cycles are tightly coupled at various spatial and temporal scales. The water cycle has a profound influence on the amount of GPP (Mystakidis et al., 2016; Wang et al., 2018; Yang et al., 2015).Precipitation and vapor pressure deficit (VPD) have been recognized as important factors influencing GPP (Beer et al., 2010; Ma et al., 2007; . Agricultural drought is an extended period of root zone soil moisture deficit that is characterized by a decrease in crop yield, reduced plant biomass, and suppressed agricultural productivity (Anderson et al. 2011; McNally et al. 2015; Wilhite and Glantz 1985).
custom gypsum block moisture meter
It is important to accurately assess agricultural drought because of its harmful impacts on the ecosystem and economy. Soil moisture reanalysis datasets provide an important way to assess agricultural drought. In this study, the ERA5-Land surface and subsurface soil moisture was used to estimate the soil water deficit index (SWDI) in four southern provinces .Soil water deficit. This is the amount of water removed by the crop from the active rooting depth. Likewise, it is the amount of water required to refill the root zone to bring the current soil moisture conditions to field capacity. Soil water decreases as the crop uses water (evapotranspiration) and increases as precipitation (rainfall or .
In this case, soil water deficit is the ratio of general field capacity and current volumetric soil moisture content. While VWC helps clarify water balance in the ground, calculating water potential is usually more helpful because it shows how it moves from the ground to the crop. Moreover, this parameter is suitable for specifying whether .
Both low soil water content (SWC) and high atmospheric dryness (vapor pressure deficit, VPD) can negatively affect terrestrial gross primary production (GPP). The sensitivity of GPP to soil versus .
custom gypsum board moisture meter
Soil moisture deficit is an essential element in the estimation of irrigation demands, both spatially and temporarily. The determination of temporal and spatial variations of soil moisture in a .A vital natural ecosystem balance including seed sprouting, plant nutrition and growth, water infiltration, plant transpiration, redistribution, evaporation, and percolation relies on paramount property of soil moisture. Understanding soil moisture measurement and its pattern is crucial for various important fields such as meteorology, hydrology, agriculture, weather, and climate .soil moisture deficit in the root zone during various stages of the crop growth cycle will have a profound impact on crop yield. For example, a 10% water deficit during the tasseling, pollination stage of corn could reduce the yield by as much as 25% (Hane and Pumphrey, 1984). Hence, the development of a reliableSoil moisture percentiles are based on the period from 1895 to the most recent soil moisture records. Learn more. Soil moisture data from the National Weather Service's Climate Prediction Center were available in GeoTIFF .
The translation from meteorological drought (i.e., precipitation deficit) to soil moisture drought depends on numerous processes that affect the surface water balance; but, to leading order, soil moisture drought can be viewed as the result of the time-integrated balance between the precipitation deficit and subsequent water losses from the . Soil Moisture Deficit. August, like June and July, is a dry month. Potential evapotranspiration still exceeds precipitation and the difference is a -42 mm. Up until this month there has been enough water from precipitation and what is in storage to meet the demands of potential evapotranspiration. However, August begins with only 16 mm of water . The use of soil moisture probes represents the technological improvement. We provide improvements in the methodology as follows. Regarding data, we employ a field-size study, instead of plots, where the irrigation decision is determined by the moisture level in the soil measured through a soil moisture probe.Soil moisture deficit. Share. Download. Description In 2000-2019, soil moisture in the growing season was several times below the long-term average in the EEA member countries plus the United Kingdom. The largest soil moisture deficits occurred in 2003, 2017 and 2019, affecting over 1.45 million km 2 in 2019. Soil moisture content was also low .
what factors affect soil moisture
Using this long-term median, maximum and minimum soil water, weekly percentage soil moisture deficit or excess for 98 years (1901–1998) was calculated as: (1) S D i, j = S W i, j − MS W j MS W j − min S W j × 100, if S W i, j = MS W j S D i, j = S W i, j − MS W j max S W j − MS W j × 100, if S W i, j > MS W j where SD i,j is the .The maximum soil water deficit (MSWD) (also . referred to as the management allowable deficit) is the amount of water stored in the soil that is readily available to the plant. The crop should be irrigated once this amount of moisture has been removed from the soil. Once depleted this is the amount that must be
The most significant characteristic of a hot drought is that the warm and dry atmosphere exacerbates the scarcity of precipitation and leads to a loss of soil moisture (SM), amplifying its effects on vegetation (Breshears et al., 2009; Williams et al., 2020).This coupling of high vapor pressure deficit (VPD) and low SM significantly increases the risk of vegetation .Soil Moisture Deficit Index (SMDI) Index name: Soil Moisture Deficit Index (SMDI). Ease of use: Red. Origins: Developed from research at the Texas Agricultural Experiment Station, United States by Narasimhan and Srinivasan in 2004. Characteristics: A weekly soil moisture product calculated at four different soil depths, including the total soil column, at 0.61, 1.23 and 1.83 .China is frequently subjected to local and regional drought disasters, and thus, drought monitoring is vital. Drought assessments based on available surface soil moisture (SM) can account for soil water deficit directly. Microwave remote sensing techniques enable the estimation of global SM with a high temporal resolution. At present, the evaluation of Soil Moisture Active Passive .The current soil moisture deficit is the difference between the TAW and the actual soil moisture status in the root zone depth in field. There are many methods available to measure the current soil moisture deficit. These methods include measuring soil moisture electronically using neutron gauge or resistance blocks, measuring by physical .
Atmospheric aridity (vapor pressure deficit, VPD) and soil moisture (SM) deficit limit plant photosynthesis and, thus, affect vegetation carbon uptake. The strong correlation between SM and VPD makes it challenging to delineate their relative contributions to regional vegetation productivity. Addressing this gap is vital to understand the .
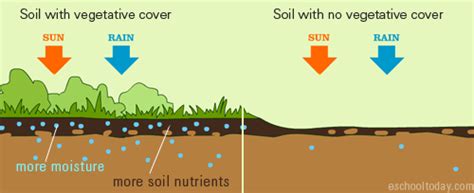
soil moisture deficit definition
custom göksu soil ph & moisture meter
WEB15 de ago. de 2023 · Once you have an invite link or are ready to pick an app from Airport, here’s how you can install them on your iPhone. Step 1: Download the TestFlight app from the App Store on your iPhone .
soil moisture deficit|how is soil moisture measured